Article Provided By Spine Associates
Lumbar spondylosis is a problem caused by the breakdown of the bones in the spine. Often, osteoarthritis is the cause of this breakdown, which generally occurs near the neck, in the cervical vertebrae, but can occur anywhere in the spine. Generally, spondylosis is symptomatic and symptoms may include pain in the back, legs or hips.
Symptoms of Spondylosis
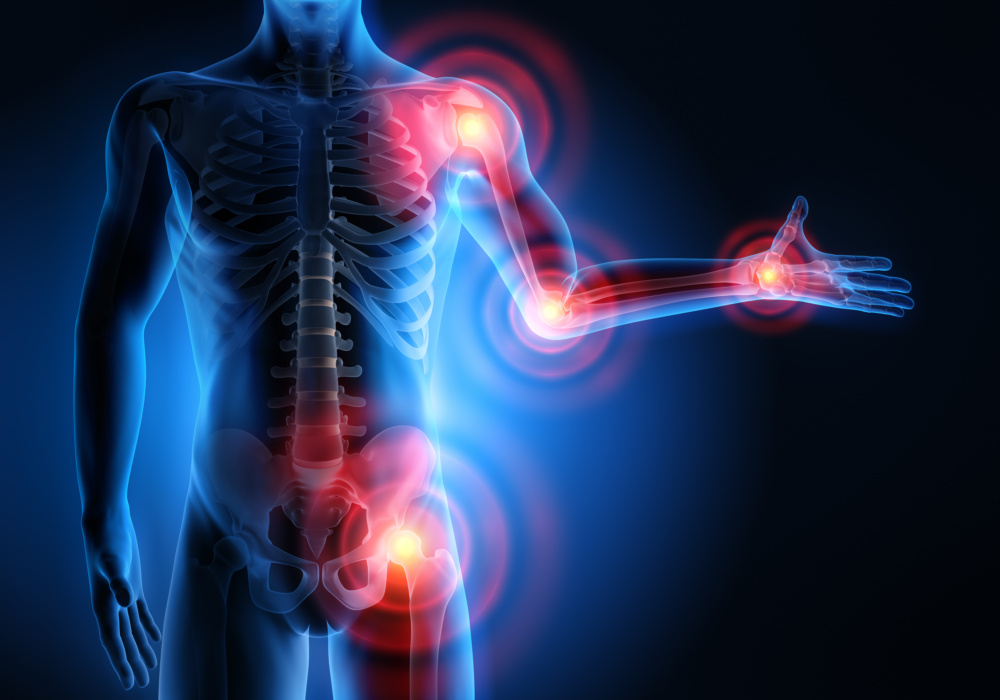
There are three different types of spondylosis. The most common type of spondylosis is characterized by neck pain. The second type involves pain in the arms. The third type involves problems with the hips and/or problems due to walking. Some patients exhibit all three types of symptoms, which will include pain in the hip or legs.
Causes of Pain
Pain is caused by spinal cord compression. In some cases, lumbar spondylosis causes this compression to occur. This condition, called myelopathy, is a result of either arthritis, old age, disk degeneration or the dehydration of disks in the spine, resulting in increased pressure on the spine. When the spinal cord becomes compressed, walking can become difficult and may be accompanied by hip pain.
Arthritis and Spondylosis
Arthritis is a common cause of spondylosis, as it causes the bones in the spine to grow abnormally and creates ridges in the disks of the spine. When the spinal cord becomes damaged, pain can occur in the back, legs, and hips. However, arthritis itself is often a cause of bone and joint pain. Since both arthritis and spondylosis cause similar types of pain, it may be difficult to determine which of these two specific conditions is actually causing hip pain.
Symptoms
Symptoms of lumbar spondylosis vary from patient to patient. In addition to hip pain, stiffness and tingling of the hip or other extremities may occur. Pain in the hips and/or other bones and joints may be exacerbated when moving.
Treatment
Pain management methods for lumbar spondylosis include immobilization, back braces, and physical therapy. Drugs, including NSAIDs (mon-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), may also be purchased over-the-counter or prescribed to deal with the pain. In rare cases, surgery and/or spinal fusion (an operation to help the vertebrae in the spine fuse) may be recommended. Surgery is usually only recommended if the symptoms are not treatable or manageable and/or if the hip pain becomes a disabling factor that dramatically interferes with quality of life.





Recent Comments